12V DC circuit protection is a vital safety measure for any off-grid adventure, ensuring your 12-volt direct current (DC) power supply remains reliable and secure. Whether you're hitting the open road, harnessing solar power, or powering small electronics, robust circuit protection is essential.
What is DC Circuit Protection & Why is it Important?
Having reliable 12V DC circuit protection is crucial—it prevents serious issues like component damage, overheating, and electrical fires in systems that rely on a 12-volt direct current. Without quality protection, even minor faults can escalate rapidly.
For instance, if a wire short circuits due to wear or a loose connection, the current can surge to dangerous levels, causing the wire insulation to melt or ignite. In automotive systems, inadequate protection could lead to malfunctioning essential components, such as the ignition or lighting, creating unsafe driving conditions.

Similarly, in a solar power system, an unprotected circuit could overheat, damaging sensitive electronics and posing a fire risk. Additionally, power surges or spikes in unprotected circuits can inflict permanent damage on batteries, inverters, or other expensive components.
By limiting excessive current, circuit protection devices like fuses and breakers safeguard both the equipment and the users, reducing the risk of costly repairs and maintaining the system’s overall reliability and safety.
Circuit Breakers vs. Fuses
When it comes to your circuit protection, there are a few options you can choose from, but the most common for 12V camper/caravan/canopy systems will be circuit breakers or fuses. While both options break up your circuit and provide key safety features, there are a few differences between the two that you’ll need to consider.
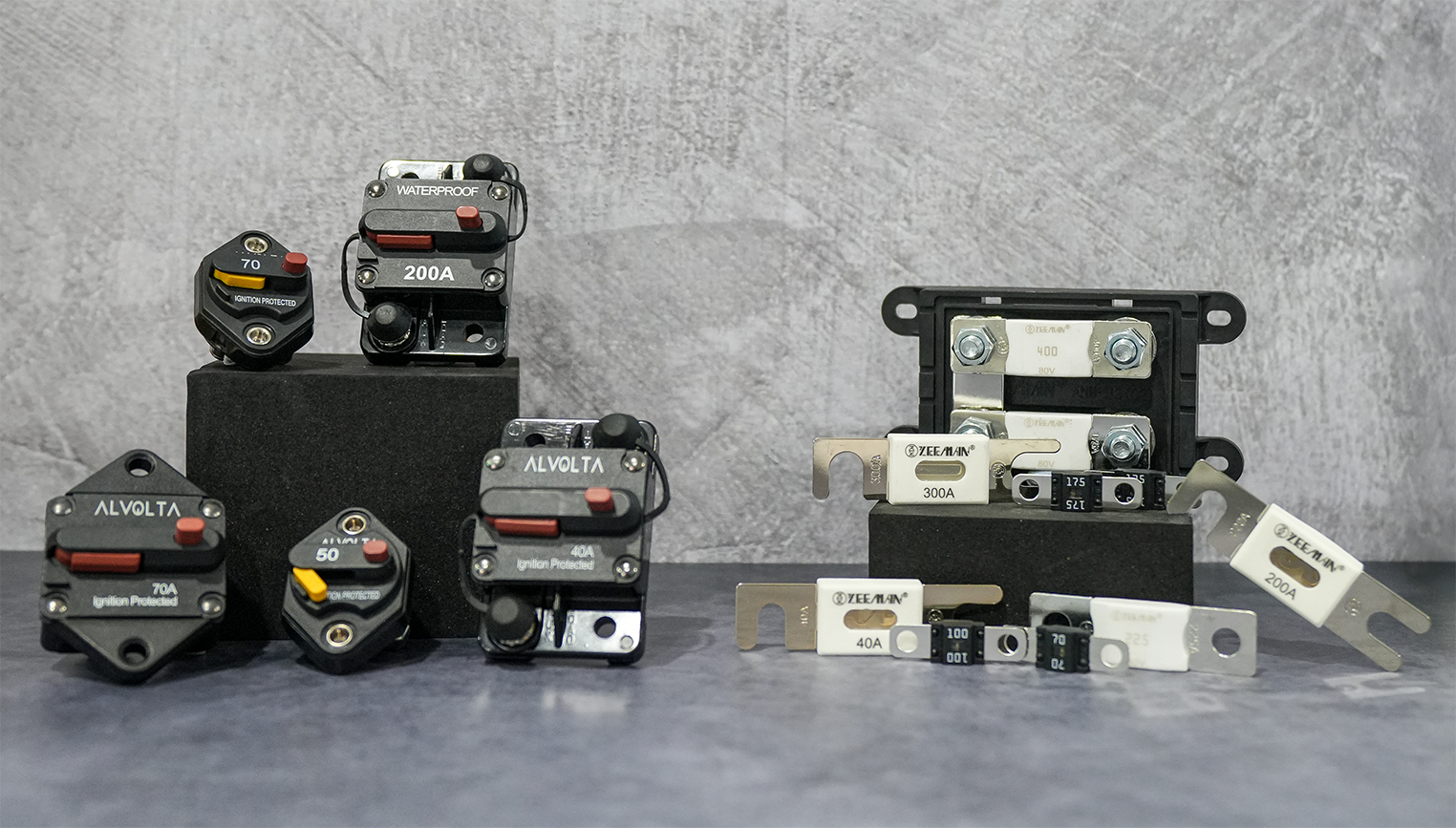

Breakers:
Circuit breakers are small switch-like devices that will ‘trip’ when the circuit has exceeded the current limit. This ‘trip’ breaks the circuit, stopping the current flow. Once the circuit breaker has been ‘tripped’, it can be reset automatically or manually, and the current will flow again. This is one of the benefits of circuit breakers in comparison with fuses, they can be used and reused, prolonging the time between when you need to replace your components.
Due to their design, circuit breakers are key in fault finding within more complex systems, as you can trip them one by one to uncover any faults. Additionally, they can be used simply as manual switches, which can provide an extra level of circuit control and protection.
While circuit breakers offer convenience, reusability and versatility, they present a more significant upfront cost than their fuse counterpart, especially for higher-current systems.

Fuses:
Fuses are simple devices that link an electrical circuit. Typically consisting of two contact plates connected by a thin strip or wire (resistor), fuses can come in a wide variety of sizes and amperages for different applications. When a circuit has exceeded the current limit, heat is generated by the excess current, which will melt the resistor inside the fuse breaking the circuit - this is known as blowing a fuse.
Unlike circuit breakers, once a fuse has been blown, it will need to be replaced before the current can flow through the circuit again. While this means they aren’t reusable, a benefit of fuses is that they are significantly cheaper upfront than their circuit breaker counterparts and a lot easier and quicker to replace.
Additionally, fuses have a high short-circuit current rating, which makes them especially useful for higher-amperage systems or for protecting the current directly from your battery bank.
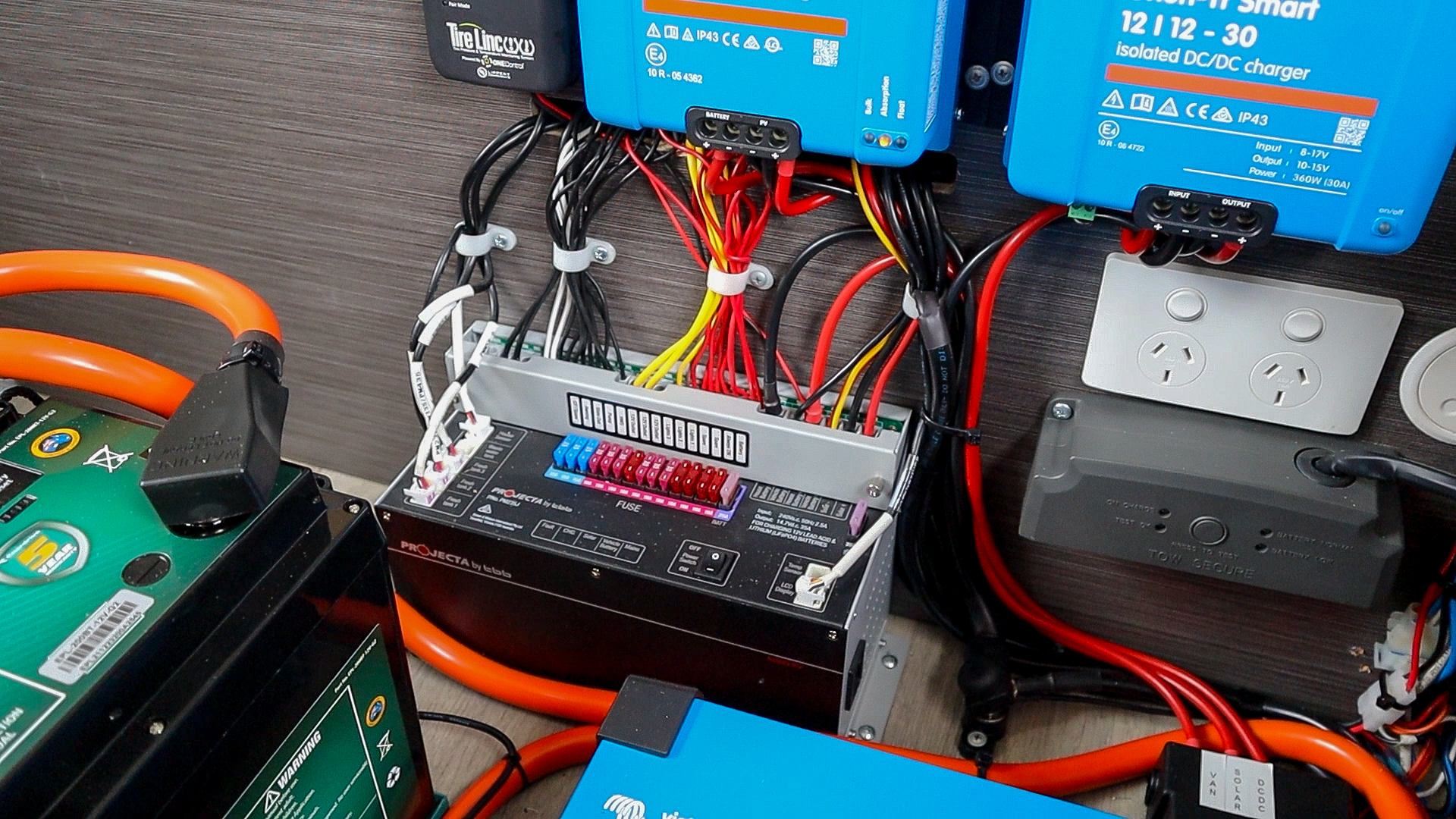
Which Component to Choose?
Choosing between circuit breakers and fuses for your 12V DC system is mostly based on the specific requirements of your setup.
If your circuit requires strong protection from your battery bank, or you’re looking for circuit protection for a high-amperage system that doesn’t break the bank, then fuses might be the solution for you.
For smaller loads, we recommend AMI/Midi Fuses:
For larger/higher-amperage loads, we recommend AMG/Mega Fuses:
If your setup requires you to regularly check for faults or you need to be able to manually disconnect from your loads, then circuit breakers might be a better option for you.
For smaller loads, we recommend 255 Series Circuit Breakers:
For more significant loads, we recommend Manual Reset Circuit Breakers:
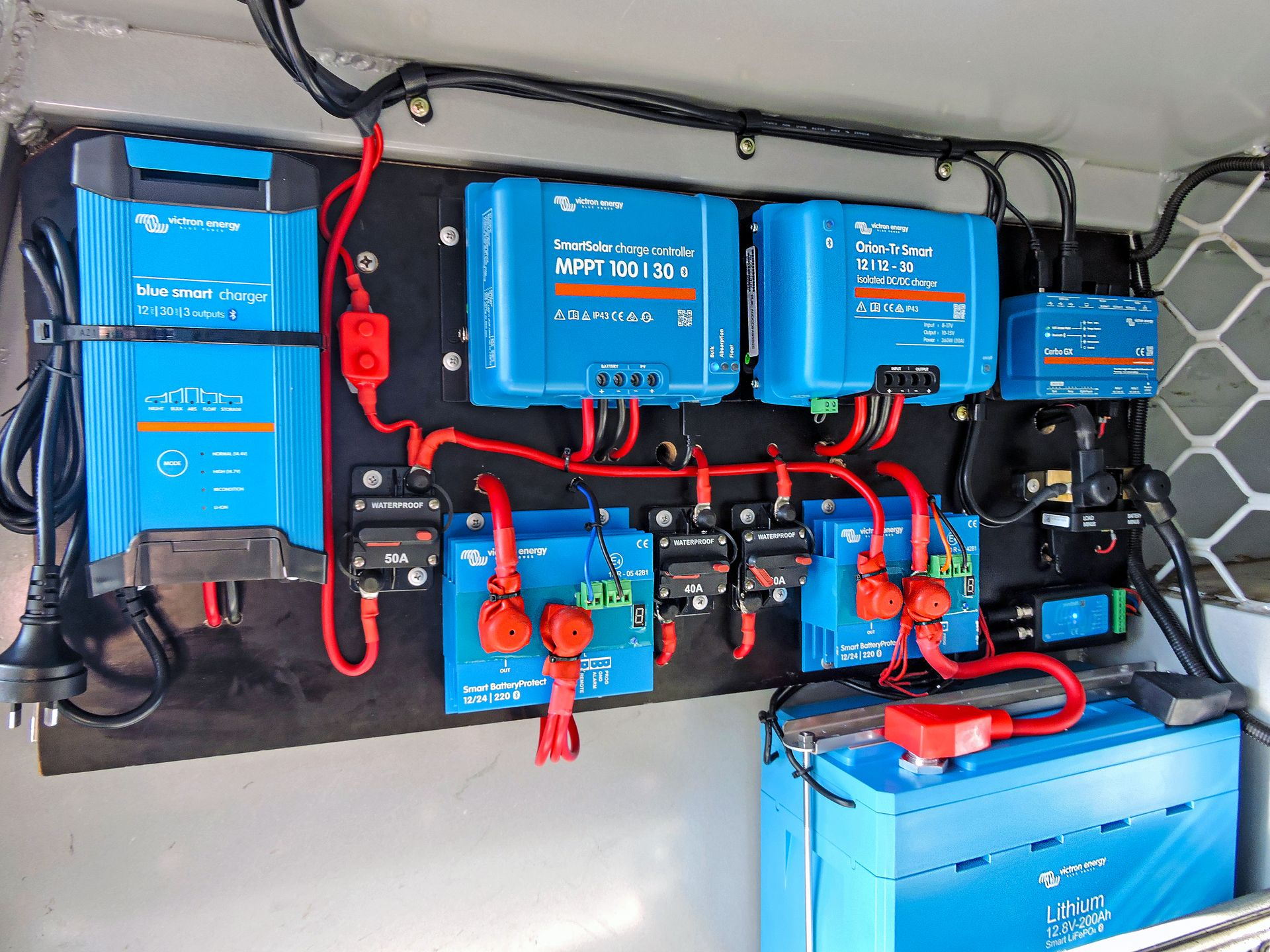
It is also important to consider the other components of your system. Some inverters, DC-DC converters and MPPTs can specify certain protection that they require within a system.

Sizing Your Protection
Whether you choose fuses or circuit breakers for your system, the way you determine the size you’ll need is the same. As the main goal of your circuit protection is to protect the cable, you should always size your breaker or fuse according to the cable’s rating.















DC Circuit Protection Guide